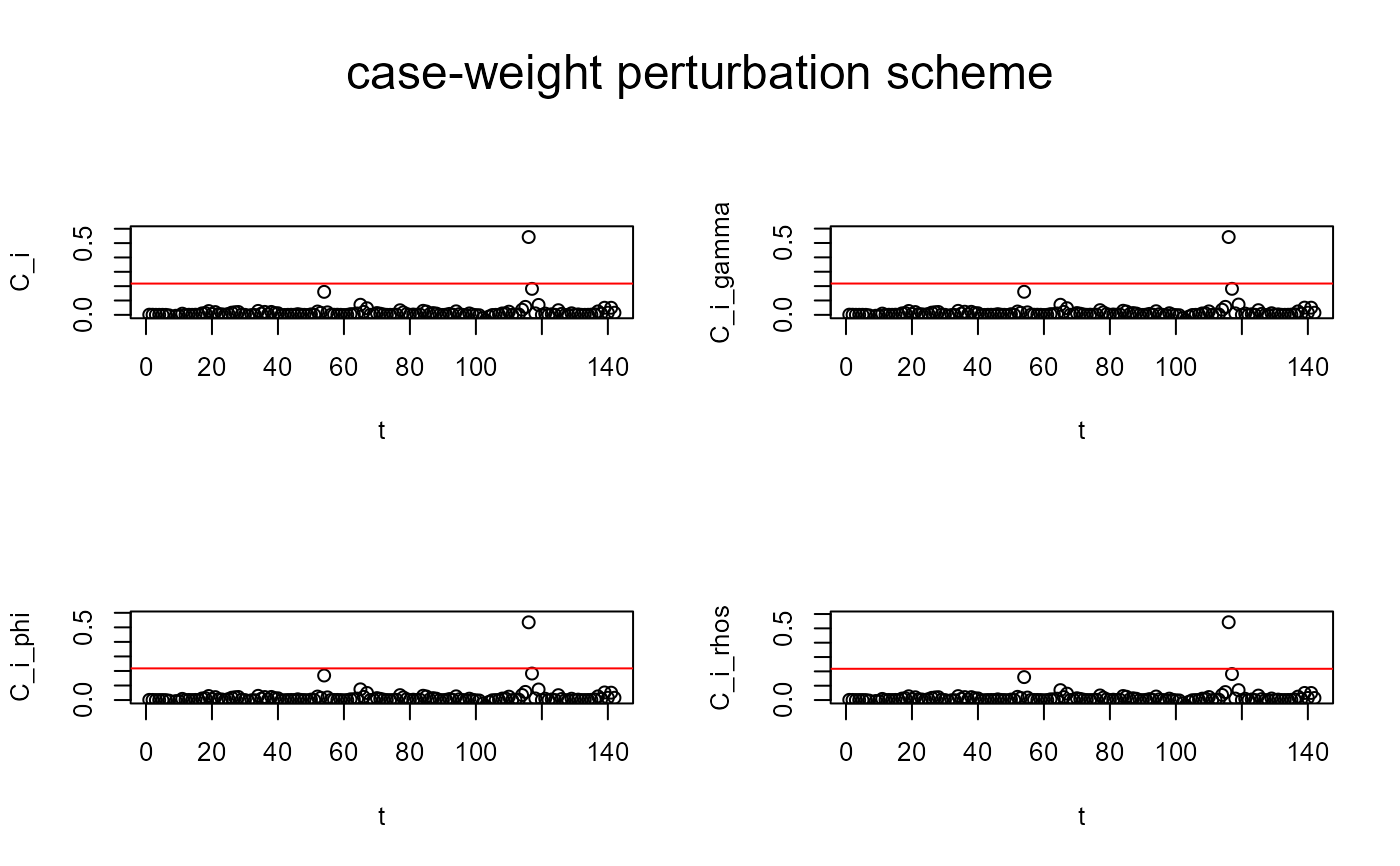
Local influence plots of the object `aplms()`
Source:R/influenceplot.aplms.R
influenceplot.aplms.RdTakes a fitted `aplms` object and outputs diagnostics of the sensitivity analysis by assessing the effects of perturbations in the model and/or data, on the parameter estimates. The `case-weight`, `dispersion`, `response`, `explanatory`, and `corAR` perturbations are available.
Usage
influenceplot.aplms(
model,
perturbation = c("case-weight", "dispersion", "response", "explanatory", "corAR"),
part = TRUE,
C = 4,
labels = NULL
)Arguments
- model
an object with the result of fitting additive partial linear models with symmetric errors.
- perturbation
A string vector specifying a perturbation scheme: `case-weight`, `dispersion`, `response`, `explanatory`, and `corAR`.
- part
A logical value to indicate whether the influential analysis is performed for \(\gamma\), \(\phi\) and \(\rho\).
- C
The cutoff criterion such that \(C_i > \bar{C_i} + C*sd(C_i)\) to detect influential observations.
- labels
label to especify each data point.
Examples
data(temperature)
temperature.df = data.frame(temperature,time=1:length(temperature))
model<-aplms::aplms(temperature ~ 1,
npc=c("time"), basis=c("cr"),Knot=c(60),
data=temperature.df,family=Powerexp(k=0.3),p=1,
control = list(tol = 0.001,
algorithm1 = c("P-GAM"),
algorithm2 = c("BFGS"),
Maxiter1 = 20,
Maxiter2 = 25),
lam=c(10))
influenceplot.aplms(model, perturbation = c("case-weight"))
#> [1] "case-weight perturbation scheme"